BIOLOGY LECTURE ON CELL DIVISION(MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS)
CELL DIVISION
CELL CYCLE-
When cell divides.It synthesise its components including genetic material in duplicate. After division This passes to DAUGHTER CELLS.
Sequence of events by which cell duplicate its contents & divides into two called CELL CYCLE.
IMPORTANCE IN EUKARYOTES-
From single cell trillions of cells develop.Rate & no. officer division vary.In adult tissues like bone marrow division is continuous.In fully formed organism less division occurs.
CELL CYCLE
It Has two periods:
1-INTERPHASE :- Period of rest or RESTING STAGE.Preparatory phase for cell division.
2-MITOSIS :-
Three processes occurs during this phase:
- REPLICATION OF DNA & SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS AS HISTONES.
- IN ANIMALS-DUPLICATION OF CENTRIOLE-Two daughter centrioles formed at right angle to each other.
- SYNTHESIS OF ENERGY RICH COMPOUNDS-Provides energy for mitosis & synthesis of proteins
MITOSIS
ITS DIFFERENT PHASES & SIGNIFICANCE :
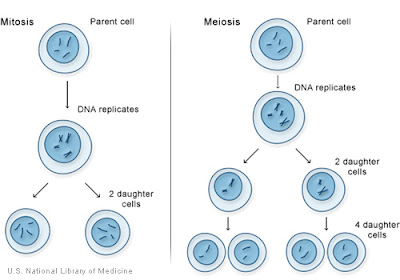
MITOSIS :- It Is a process of cell division in which chromosomes are duplicated & distributed equally in daughter cells.
It has five PHASES:-
- PROPHASE
- PROMETAPHASE
- METAPHASE
- ANAPHASE
- TELOPHASE
PROPHASE
- NUCLEUS become spheroid.
- CHROMOSOMES shortens& thickens.become stainable.
- DOUBLE STRANDED nature is visible.
- TWO CHROMATIDS CALLED SISTER CHROMATIDS held together by centromere.
- CENTROSOME duplicated during INTERPHASE starts moving towards opposite poles of cell.
- SPINDLE made of microtubules begins to be formed between two poles.ASTERS surrounds the centriole & spindle together forms mitotic apparatus .
PROMETAPHASE
- NUCLEAR MEMBRANE disappears.
- CYTOPLASM & NUCLEOPLASM MIXES.
- CHROMOSOMES are attached to spindle through CENTROMERE. It is called EUMITOSIS.
- When nuclear membrane does not disappear as in protozoa is called INTRANUCLEAR MITOSIS.
METAPHASE
- CHROMOSOMES are lined up in one plane form equatorial plate.
- CENTROMERE lies on equatorial plane & small chromosomes are in CENTRE & larger on periphery.
ANAPHASE
- SISTER CHROMATIDS begins to separate from each other starting at centromere.
- DAUGHTER CHROMOSOMES in two sets starts migrating towards poles.
- SPINDLE FIBRES shortens.
TELOPHASE
- DAUGHTER CHROMOSOMES reached the opposite poles & spindle disappears.
- NEW NUCLEAR MEMBRANE formed around chromosomes .NUCLEOLI reappears at constrictions called nucleolar organiser.
- TELOPHASE is reverse of PROPHASE.
- CHROMOSOMES uncoiled & less compact loose their staining ability.
CYTOKINESIS-
- CONSTRICTION OR CLEAVAGE appears.
- SPINDLE breaks down.TWO DAUGHTER CELLS forms.DIVISION of CYTOPLASM is called CYTOKINESIS.IF division is without cytoplasmic division IT IS SYNCYTIUM large no of nuclei present in single cell.
AMITOSIS-
DUMBELL shaped cleavage. No spindle.NUCLEI of unequal size in PROTIST.
SIGNIFICANCE :-
- EQUAL DISTRIBUTION of chromosomes among daughter cells.
- SURFACE/VOLUME RATIO restores.As cell increases in size surface area becomes less .BY repeated division cell becomes smaller in size & surface volume ratio restored.
- REPAIR of body takes place by addition of cells by mitosis EX epidermis,lining of gut,RBC are replaced
- DIFFERENTIATION due to multicellular condition.
- GROWTH of organism is due to mitosis.
MEIOSIS
THIS TYPE OF DIVISION happens in GERM CELLS which forms GAMETES [ SPERM & OVA] in SEXUALLY REPRODUCING ORGANISM.
There are two types of division in meiosis MEIOSIS 1 & MEIOSIS 2
NO OF CHROMOSOMES PER CELL REDUCED BY HALF DURING FIRST MEIOTIC DIVISION- HOMOLOGOUS PAIR OF CHROMOSOMES SEPARATE & distributed into separate cells.
D URING SECOND MEIOTIC DIVISION SISTER CHROMATIDS SEPARATE distributed to daughter cells.
BOTH DIVISIONS have 4 phases :
- PROPHASE
- METAPHASE
- ANAPHASE
- TELOPHASE
IN MEIOSIS-IMPORTANT STEPS ARE :
- NO DNA REPLICATION
- PAIRING &FORMATION OF CHIASMATA& CROSSING OVER
- SEGREGATION OF HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES
- SISTER CHROMATIDS SEPARATES.
1st MEIOTIC DIVISION
PROPHASE - 1
- LEPTOTENE
- ZYGOTENE
- PACHYTENE
- DIPLOTENE
- DIAKINESIS
1. LEPTOTENE-Each chromosome condensed to produce a long thread,attached at both of its end to nuclear envelop via a structure called ATTACHMENT PLATE. It appears like single stranded.
2. ZYGOTENE-PAIRING of HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES occurs.Process is called SYNAPSIS.[ONE chromosome from each parent.]ZIPPER like side by side in three ways:
- proterminal pairing -It starts at terminal goes towards centromere.
- procentric pairing-It starts at centromere goes towards the end.
- random pairing-It may be at many points towards the ends.
TWO chromosome come close by a ladder like structure called SYNAPTONEMAL COMPLEX. It is called BIVALENT contains four chromatids called a TETRAD.
3. PACHYTENE -Large recombination nodules appear at intervals on synaptonemal complex.NON sister chromatids exchange segments with each other.[CROSSING OVER]
4. DIPLOTENE-Separation of chromosomes occurs.Homologous chromosomes remain attached at one or more points this point of attachment called CHIASMATA.
5. DIAKINESIS- RNA SYNTHESIS stops.CHROMOSOMES condense & thickens attached to nuclear envelop.SISTER CHROMATIDS attached at centromere. Non sister chromatids are in contact with each other near telomere.
METAPHASE 1-
1.Bivalents are arranged in plane of equator forming equatorial plate.CENTROMERE of each chromosome on opposite poles.
ANAPHASE 1-
Two members of bivalent repel each other & move towards the opposite poles.EACH POLE receives half a number of chromosomes[n number of chromosomes].Spindle fibres shortens.
TELOPHASE1-
NUCLEAR membrane & nucleolus in each nucleus appears.TWO daughter cells forms with haploid no. of chromosomes
INTRAMEIOTIC INTERPHASE-
It is a stage between telophase of first & prophase of second meiotic division.NO Replication of DNA takes place.
SECOND MEIOTIC DIVISION
It divides each haploid nucleus into two daughter haploid nuclei. FOUR CELLS forms as a result:
1. PROPHASE 2 :- Spindle formation & nuclear membrane disappears.
2. METAPHASE 2 :- Chromosomes on equatorial plate, same as in mitosis.
3. ANAPHASE 2 :- Centromere divides & two sister chromatids separate move towards poles.Each chromatid becomes a chromosome.
4. TELOPHASE 2 :- FOUR groups of chromosomes are organised into four haploid nuclei.Nucleolus reappears.Endoplasmic reticulum forms.Four cells forms.
SIGNIFICANCE-
1. It maintains constant no. of chromosomes in sexually reproducing organism.
2. Exchange of genes occurs during crossing over leads to GENETIC VARIATION among species.
3. It has impact on genetic variation due to crossing over,pairing & segregation of homologous chromosomes.










Comments
Post a Comment